Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on or within the ovaries, which play a key role in egg development and hormone production. Most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve naturally without intervention. However, some types may cause complications like pelvic pain, infertility, or pregnancy issues, particularly if they grow large or rupture. Regular pelvic examinations, including ultrasounds, are recommended for monitoring. While many cysts are asymptomatic, larger ones can cause discomfort, prompting exploration of natural remedies to alleviate symptoms or support cyst resolution, though scientific evidence for cyst shrinkage is often limited.
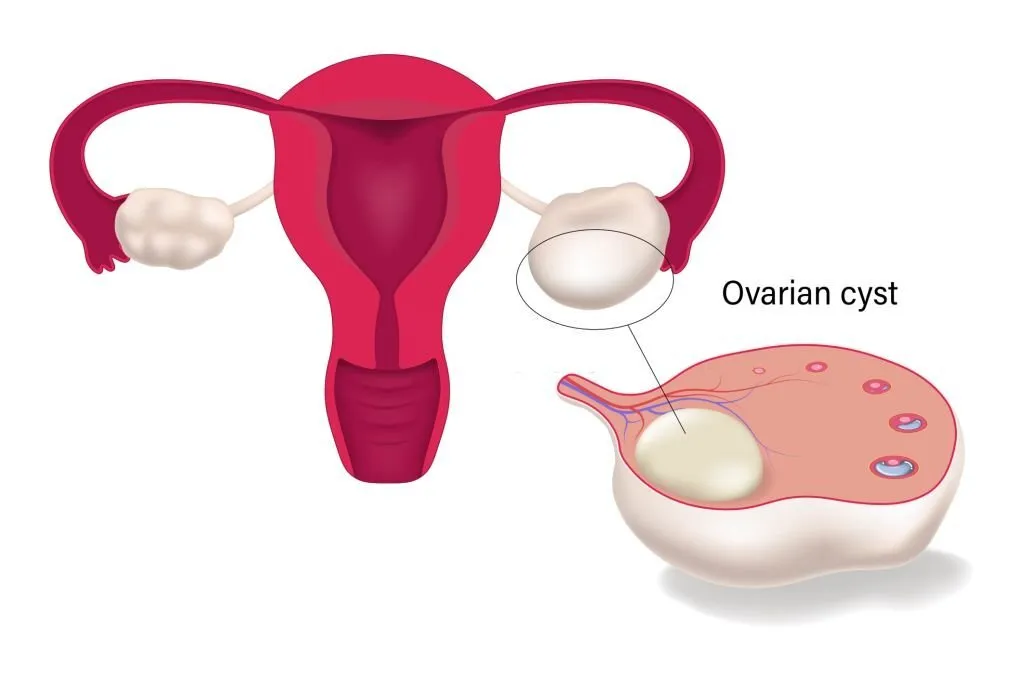
Types and Causes of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are primarily linked to menstrual cycle irregularities:
- Follicular Cysts: Occur when a follicle fails to rupture and release an egg, filling with fluid.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: Form when the corpus luteum, post-ovulation, accumulates fluid instead of regressing.
- Dermoid Cysts: Develop from germ cells, containing tissues like hair or skin.
- Cystadenomas: Grow on the ovary’s surface, filled with watery or mucous material.
- Endometriomas: Result from endometrial tissue attaching to the ovaries, often linked to endometriosis.
Other causes include hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated estrogen levels, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and, rarely, infections or ovarian tumors. Understanding the cyst type is crucial for effective management.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, but larger or problematic cysts may cause:
- Dull or sharp pelvic pain, often on one side.
- A sensation of heaviness, fullness, or pressure in the lower abdomen.
- Bloating or abdominal swelling.
- Pain during intercourse or bowel movements.
- Irregular menstrual cycles or spotting.
Severe symptoms, such as sudden intense pain or fever, may indicate complications like cyst rupture or torsion, requiring immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Diagnosing ovarian cysts typically involves:
- Pelvic Exams: To detect abnormalities in the ovaries.
- Ultrasound: To visualize cyst size, type, and location.
- Blood Tests: To check for hormonal imbalances or tumor markers (e.g., CA-125).
- Laparoscopy: For detailed examination in complex cases.
Regular monitoring helps assess whether cysts resolve naturally or require intervention, especially for women with risk factors like PCOS or endometriosis.
Natural Remedies for Ovarian Cysts
Natural remedies aim to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, or support cyst resolution, though evidence for shrinking cysts is limited. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting remedies, especially for persistent symptoms.
Castor Oil
Castor oil has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immune-boosting properties. It may reduce pelvic pain and support tissue health. Apply a small amount to the lower abdomen or use a castor oil pack (soak wool flannel, apply, cover with plastic, and use a hot water bottle for 30-60 minutes). Use 3-4 times weekly, avoiding during menstruation.
Ginger
Ginger’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may alleviate pelvic pain and restrict abnormal cell growth, potentially aiding cyst management. Consume as ginger tea (steep fresh ginger slices in hot water), juice, or supplements (500 mg daily). Regular use may also support PCOS symptom relief.
Beet Root
Beet root’s betacyanins offer antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and detoxifying benefits, potentially supporting ovarian health. Blend beet juice with apple or carrot for daily consumption (1 cup). Its liver-cleansing properties may help regulate hormones.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar may lower blood sugar, potentially benefiting PCOS-related cysts, though evidence for cyst shrinkage is lacking. Mix 1-2 tablespoons in water and drink daily. Avoid undiluted use to prevent digestive irritation.
Essential Oils
Lavender, frankincense, geranium, or cypress oils, mixed with castor oil (3-5 drops per teaspoon), may reduce inflammation and pain. Apply topically to the lower abdomen twice daily, massaging gently. Perform a patch test to avoid skin reactions.
Applying Heat
Heat therapy alleviates pelvic pain by increasing blood flow. Apply a heated towel (microwaved to a safe temperature) or take a warm bath (15-20 minutes) 2-3 times daily. Ensure the temperature is comfortable to avoid burns.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
Lifestyle adjustments can support ovarian health and reduce cyst risk:
- Reduce Estrogen Exposure: Avoid xenoestrogens in plastics, non-organic foods, soy, parabens, and synthetic chemicals in cosmetics or body washes.
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Emphasize whole foods, omega-3s, and antioxidants (e.g., berries, leafy greens) while limiting processed foods and sugars.
- Exercise: Moderate activity like yoga or walking improves circulation and hormonal balance.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation or deep breathing reduce cortisol, which can exacerbate hormonal imbalances.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake supports detoxification and overall health.
Importance of Medical Consultation
While natural remedies may alleviate symptoms, they are not a substitute for medical evaluation. Persistent or severe symptoms, such as intense pain or irregular bleeding, require prompt medical attention to rule out complications like cyst rupture or ovarian torsion. Healthcare providers may recommend watchful waiting, hormonal treatments, or surgery for problematic cysts.

Conclusion
Ovarian cysts, common fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries, are often benign and resolve naturally. However, larger or symptomatic cysts can cause pelvic pain, bloating, or complications, necessitating monitoring and management. Natural remedies like castor oil, ginger, and beet root may alleviate symptoms or support ovarian health, but scientific evidence for cyst shrinkage is limited. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing estrogen exposure and adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, are crucial for prevention and symptom management. Women with persistent symptoms should seek professional medical advice to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment, combining natural and medical approaches for optimal outcomes.



